What is SOAR
(Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response)?
SOAR Defined
Security Orchestration, Automation and Response (SOAR) is a cybersecurity solution that integrates with disparate security tools to centralize alerts and automate investigation and response for cyber threats such as malware and phishing.
Gartner, who coined the term SOAR in 2016, defines SOAR as, “technologies that enable organizations to collect security threats data and alerts from different sources, where incident analysis and triage can be performed leveraging a combination of human and machine power to help define, prioritize and drive standardized incident response activities.”
Why do Security Teams Need SOAR?
In a security environment where having dozens of tools is the norm, many challenges arise. These include data and functional silos, constant screen-switching, an overwhelming number of alerts, and stealthy threats that evade detection. With cybersecurity talent at a premium, SOAR emerged as an automation-powered solution to all these problems.
The central promise of SOAR is that it reduces manual tasks, administrative toil, and repetitive busywork, enabling security teams to spend more of their time on real threats.
How Does SOAR Work?
Integrates with Other Tools
The power of SOAR platforms comes from their ability to integrate with other tools and systems. A broad range of fully featured integrations enable SOAR to execute its other functions by orchestrating actions across the environment. Some SOAR integrations are prebuilt by vendors, while others are coded in the tool by users.

Centralizes Alerts and Intelligence
SOAR is not a detection tool. It ingests security alerts from other tools, such as SIEM, EDR, and email protection systems. These aggregated alerts become events or incidents in the SOAR tool, which can then be enriched and investigated.
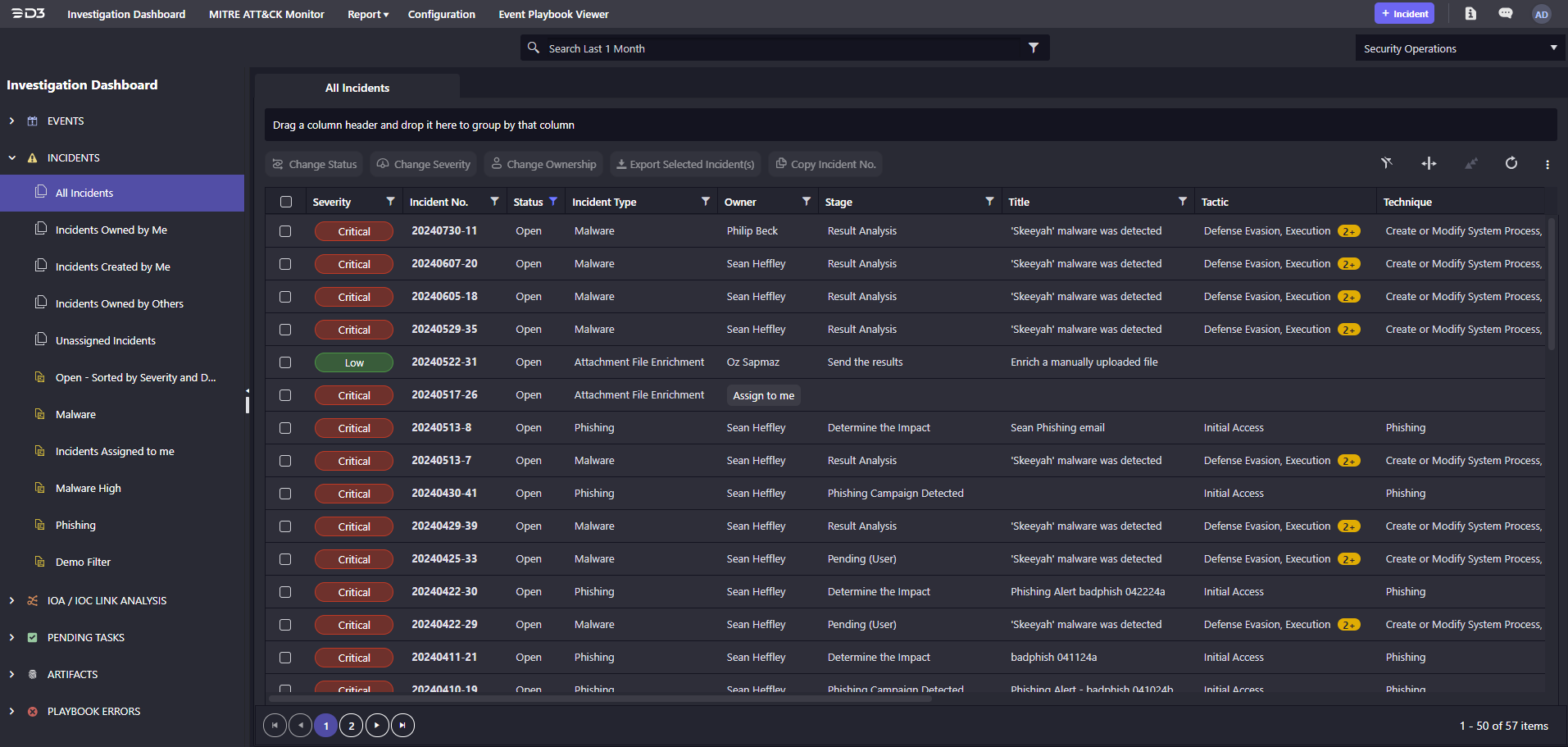
Enriches and Prioritizes Threats
SOAR automates the time-consuming, repetitive process of enriching alerts with contextual information, such as the results of reputation checks on implicated artifacts. SOAR tools can triage alerts based on enrichment and other factors, providing users with an assessment of the risk posed by an alert.
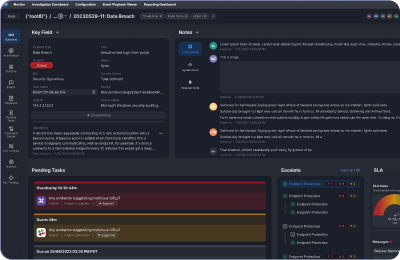
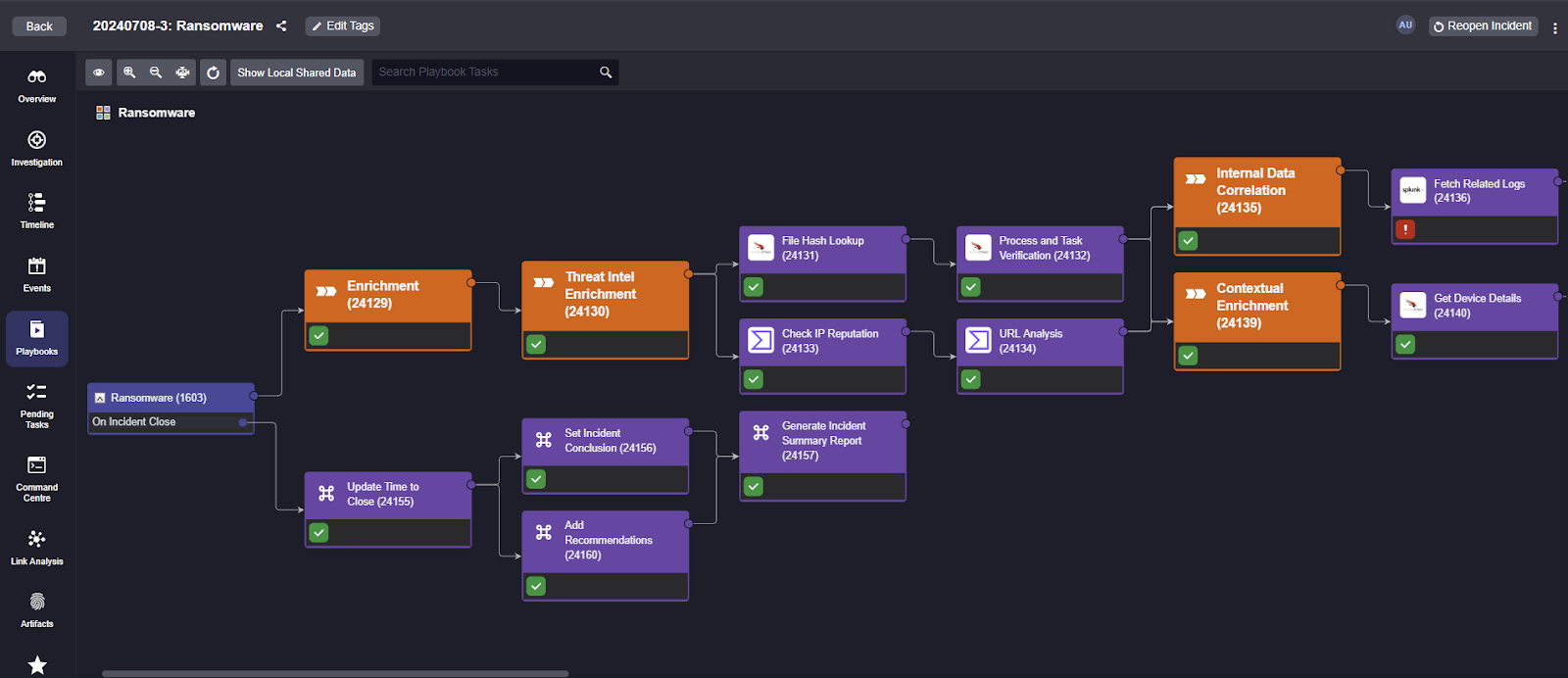
Orchestrates Incident Response
SOAR tools enable users to execute incident response workflows to investigate and mitigate cybersecurity threats, usually in the form of playbooks. SOAR playbooks may be entirely automated, or they may have some manual tasks or decision points for the user.
Generates Reporting
SOAR tools generally provide dashboards with information on day-to-day operations, such as the number of open incidents, as well as detailed reports on past incidents, team performance, performance against benchmarks, and more. SOAR tools can often generate and distribute scheduled reports automatically.
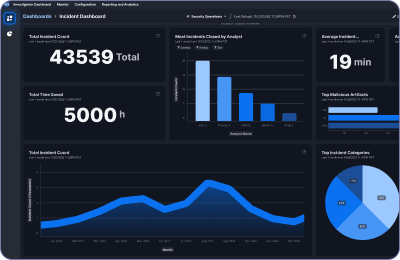
Top 10 Benefits of SOAR
Faster Response Time
The longer a security incident goes undetected, the more damage it does. One of the primary benefits of SOAR is how it drastically shortens the time it takes to detect and respond to incidents. SOAR automates alert enrichment, orchestrates actions across tools, and automates incident response playbooks.
Improved Resiliency
By combining the powers of your entire stack, eliminating blind spots, and improving efficiency through automation, SOAR increases organizations’ ability to withstand attacks. Minor incidents can be handled quickly and major incidents can be identified and mitigated before they cause damage.
Analyst Retention
Recruiting, hiring, and training security personnel requires time and resources. So it’s important to keep them happy and engaged with their work. Too many SOC analysts burn out from handling a high volume of unimportant alerts every day. It gives them little opportunity to apply and develop their skills. SOAR cuts down on busywork and repetitive tasks, enabling analysts at all tiers to stay focused on real threats.
Minimized Manual Work
Manual inputs are important for key decision points, but automation is much better suited to handling the simple, repetitive tasks that can overwhelm the typical SOC. Automation frees up that time so analysts can focus on real threats.
Optimized Threat Intelligence
Most SOCs have access to a wealth of threat intelligence, but struggle to put it to use efficiently. SOAR automatically aggregates threat intelligence to enrich incidents and assess risk.
Lowered Costs
SOAR enables security teams to accomplish much more, without adding headcount. User-friendly automation features reduce the need for expensive professional services, consultants, and coders.
Reduced Impact of False Positives
Without SOAR, Tier 1 security analysts can easily spend the majority of their time on alerts that turn out to pose no actual risk. By automating triage, correlation, threat intelligence enrichment, and risk scoring, SOAR can quickly identify false positives, and in many cases, automatically resolve them.
Enhanced Integration Capabilities
Today’s SOCs often comprise dozens of tools, but they aren’t designed to work well together. SOAR enables seamless interoperability, creating a unified security stack that moves at machine speeds.
Supports Best-of-Breed Tooling
Vendor-agnostic SOAR tools make it easy for security teams to integrate their preferred tools, instead of centralizing on a single vendor’s suite.
Easier Staff Onboarding
When you integrate your tools with SOAR, new team members primarily need to learn just that one interface, since they can orchestrate functions in other tools. Codifying best practices in playbooks also helps upskill junior analysts and bring new hires up to speed faster.
Key SOAR Use Cases
SOAR makes it easier to handle phishing threats at large volumes. With just a few clicks, it quickly checks each possible phishing incident, examines suspicious emails, tests any harmful attachments in a safe environment, and decides the best action to take.
When an EDR identifies a potentially risky endpoint, SOAR evaluates the threat level and decides on the appropriate action. Response actions may include detonating the suspicious file in a safe location, searching for it on other endpoints, removing the file, blocking its signature, and isolating the affected endpoints.
Security teams often struggle to run regular vulnerability scans and effectively turn the results into action. SOAR streamlines this process by automating workflows triggered by vulnerability scans. When an integrated tool scans endpoints and identifies a security weakness, SOAR automatically interprets the scan report and triggers a playbook to address the vulnerability.
Beyond incident response, SOAR platforms also support threat hunting with automation and orchestration. Some SOAR platforms turn threat intelligence into automated threat hunting, search for indicators of compromise (IOCs) linked to new incidents, and monitor critical IOCs and tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs).
SOAR Buyer’s Checklist
Integrations
- Does the SOAR tool have high-quality out-of-the-box integrations with the tools you use, and might use in the future?
- Can custom integrations be easily built by users when necessary?
Ease of Use
- Does the tool make it easy to train new users?
- Are technical documentation and training materials made available for prospective buyers?
Incident Case Management
- Does the tool group together related incidents for efficient investigation?
- Does the tool identify and display links between incidents, artifacts, and IOCs?
- Does the tool retain a full audit trail of actions taken during an investigation?
- Does the tool offer a wide range of reports and metrics, with options for automated generation and distribution?
Task Management
- Does the tool make it easy for analysts to prioritize the most important tasks?
- Can users collaborate on investigations from within the tool, with the ability to share notes and track progress?
- Does the tool support information access controls that ensure compliance and security?
Playbook Capabilities
- Is there a codeless playbook editor that enables drag-and-drop playbook creation?
- Can users build and test playbooks from a single interface?
- Does the tool come with an out-of-the-box playbook library for common use cases?
Deployment
- Does the vendor provide expert support during implementation?
- Does the tool support full multitenancy to safely segregate data across sites or an MSSP’s customers?
- Can the tool dynamically scale to handle spikes in activity?
Pricing
- Does the vendor charge a predictable subscription cost?
- Will you be able to handle major incidents without being charged extra for increased usage?
Key SOAR Integrations
SIEM
SIEM tools store large amounts of log and network data but lack the playbooks and automations necessary for managing incident response. It also lacks user-friendly integrations and can’t generate important SOC metrics. SOAR improves SIEM’s investigation and response capabilities through its wide range of integrations and security automation use cases.
EDR
SOAR integrates with EDR and other endpoint protection tools to investigate and enrich potential endpoint security incidents. SOAR orchestrates a range of actions via the endpoint tool, including malware detection, file removal, blocking file hashes, stopping malicious processes from running, quarantining endpoints, and others.
Network Security
SOCs need to act quickly to block a threat when detected. SOAR tools integrate with firewalls and network detection and response (NDR) tools to orchestrate changes to firewall rules, block malicious IOCs, update blacklists, and more.
Read: Automate Network Security with the Best Independent SOAR for Palo Alto NGFW
ITSM
Organizations use SOAR and ITSM to collaborate across teams and add automation and orchestration to ITSM tickets. ITSM can escalate tickets to SOAR for threat intelligence enrichment and investigation. Conversely, if an IT task requires an automation workflow, SOAR can generate an ITSM ticket from a playbook.
Read: Automated Incident Response with ServiceNow and Smart SOAR
Email Security
Many major incidents start with a simple phishing email. SOAR integrates with email tools to ingest reports of suspicious emails, pull those messages from the server, and parse out IOCs for investigation. If the SOAR tool spots a harmful email, it blocks the sender and deletes that email from all company mailboxes.
Read: How to Protect Against Business Email Compromise Phishing with Smart SOAR
Messaging
SOAR integrates with email senders, notification engines, collaboration spaces and other cloud communication platforms to facilitate. Beyond communication and alerting, popular IT service integrations also include meeting management and video conferencing such as Zoom.
TIP
Threat intelligence is a key pillar of SOAR. Some SOAR tools have proprietary TIPs built in, and others can integrate with virtually any intelligence source. When a SOAR tool gets an alert, it adds more details to enrich it. It does this by checking things like files, IP addresses, and URLs against threat intelligence sources to figure out the risk.
Identity
Identity is an important element of security incidents. SOAR tools work with identity management systems, adding employee details and login history to incidents. SOAR also manages responses, such as turning off user access and requiring password changes.
Vulnerability Management
SOAR turns the information from vulnerability scans into automated response workflows. SOAR tools ingest and parse vulnerability scan reports. Next, they orchestrate tasks to remediate vulnerabilities. Finally, they search across past reports during threat hunting.
Read: Automated Incident Response with Rapid7 and Smart SOAR
MSSPs Need SOAR to Thrive
SOAR is a highly valuable tool for MSSPs who want to improve their services and increase profits. Benefits include:
Increased Client Capacity
SOAR streamlines MSSP operations just like it does for in-house SOC teams. It makes operations quicker, reduces time spent on unimportant tasks, and improves the ability to assess incoming threats. The result for many MSSPs is a significant increase in the number of clients they can support without adding to their headcount.
Scalable Security Operations
In a multitenant SOAR environment, client sites can be segregated, while still allowing MSSPs to deploy proven playbooks broadly across their client base or customize them as needed. SOAR also enables better reporting, which gives visibility to clients without tying up resources.
MDR Service Enablement
SOAR gives MSSPs the tools to do more than just handle alerts, with a full set of incident response tools. This has enabled many MSSPs to offer full-lifecycle, Tier 1-3 services. They can handle end-to-end response, instead of simply alerting the client’s team of threats. This means that MSSPs can compete with the MDR providers that have been rapidly gaining market share in the managed services space.
Vendor-Agnostic SOAR Enables Flexibility
Vendor-agnostic SOAR refers to SOAR tools that integrate equally well with any vendor’s tools, enabling buyers to orchestrate across their existing tools. SOAR vendors that produce a suite of other security tools are generally not vendor-agnostic, because they prioritize integrations with their own suite. Benefits of vendor-agnostic SOAR include the option to use best-of-breed tools, the ability to centralize all operations on one platform, and flexibility for future tool changes.
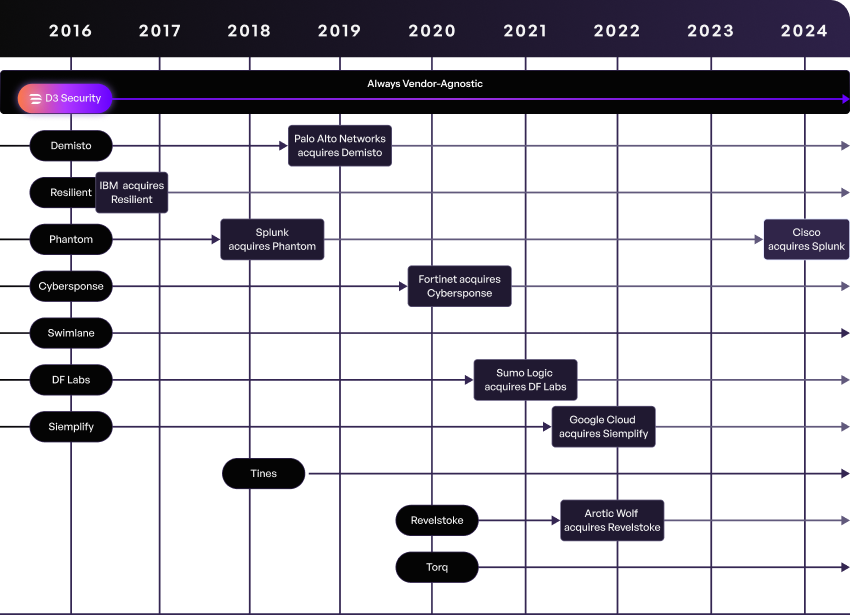
Throughout the history of the SOAR market, there have been frequent acquisitions of SOAR vendors that have shaken up the industry. Customers of these vendors have been faced with a difficult choice: accept that their previously vendor-agnostic tool will now have narrower interoperability, or rip and replace their SOAR tool with a new one. This constant state of flux has led to SOAR buyers seeking out stable vendors that they trust are in the SOAR business for the long haul.
SOAR Case Studies
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s the difference between XDR vs. SOAR?
While they work toward similar goals, there are significant differences between how XDR and SOAR function. XDR usually integrates a set of security tools from one company. On the other hand, SOAR platforms work with hundreds of different tools. SOAR platforms use playbooks to help organize how the system responds and give tasks to staff. XDR solutions typically lack this ability and instead automate single actions in response to analyzing incoming data. This is the reason many XDR vendors maintain separate security orchestration solutions in their offerings.
What’s the difference between SIEM vs. SOAR?
Despite the powerful capabilities of a SIEM, it doesn’t have the incident response, investigation, and case management tools and workflows needed to efficiently manage threats. Adding SOAR extends SecOps functionality across the full incident lifecycle, with features including:
- Alert enrichment with threat intelligence, IOC correlations, and other data
- Incident-specific, automation-powered playbooks
- Orchestrated actions across the security environment, leveraging hundreds of integrations
- Comprehensive dashboards and reporting
How has SOAR Improved in Recent Years?
SOAR tools have come a long way since their first generation, which had a reputation for not living up to the hype. Improvements in recent years include:
- Codeless playbooks, which empower users with much more flexibility and control, without relying on internal coding expertise
- Cloud scalability. Advanced SOAR tools now dynamically scale their capacity using cloud resources.
- Intelligence beyond IOCs. Today’s SOAR tools incorporate identity (e.g. user IDs, devices, and accounts) and behavior (e.g. MITRE ATT&CK techniques) data to create a truer picture of threats.
- Easier to implement and use. Thanks to more pre-built integrations, out-of-the-box playbooks, streamlined interfaces, and cloud-friendly deployment, it is easier than ever to get up and running on a SOAR tool.
Learn More About Security Automation
To learn more about AI-driven autonomous SOCs, security automation, and what makes D3’s Morpheus different from other solutions, check out these resources.