Cyber attacks are becoming more frequent and advanced these days, carried out by criminal groups offering “ransomware-as-a-service” and nation-state-backed threat groups.
To highlight this trend, let’s examine the phishing attack vector, which is the most popular attack technique for gaining a foothold in your environment. According to the latest phishing activity trends report by the Anti-Phishing Working Group (APWG), the third quarter of 2022 saw the highest-ever phishing attacks, with a total of 1,270,883 reported incidents. This marks a new record and the worst quarter for phishing that the APWG has ever recorded. According to a 2021 study, an average of three billion phishing emails are sent daily. It’s estimated that around 1.5 million new phishing websites are created each month.
When dealing with such high volumes, security automation is essential for security operations center (SOC) teams. It helps them stay one step ahead of attackers and mitigate these risks in a cost-effective and efficient manner. However, despite its growing popularity, most don’t fully grasp the scope and potential of security automation.
This guide provides a comprehensive introduction to cybersecurity automation for beginners, covering its definition, benefits, use cases, and best practices. We hope that by the end of this blog post, you understand the fundamentals of cyber security automation and how it can be leveraged to improve your overall cybersecurity posture.
What is Security Automation?
Security automation has been defined by Gartner as:
“The capability of software and systems to execute functions on their own, typically to affect other systems and applications. Security automation completes tasks without human intervention.”
The goal of cyber security automation is to improve the efficiency, accuracy, and scalability of these processes, enabling organizations to better protect their systems and data from threats without adding headcount. Security automation frees up security teams to focus on more strategic and high-value tasks and prevent burnout from alert fatigue.
Security automation refers to the use of technology to automate repetitive and time-consuming tasks. Once you have your incident response SOPs documented and defined in the form of playbooks, that institutional knowledge can be codified to automate rote tasks such as vulnerability management, incident response, and threat detection and response, to name a few use cases.
If you’re looking for a canonical definition, you can find one on our SOAR 101 page, which also gives you some context on where it fits in the category of Security Orchestration, Automation and Response (SOAR) platforms that we here at D3 Security are renowned for. More on that later.
What Are The Benefits of Security Automation?
Security automation can benefit all members of a security team, regardless of their role, whether they are a SOC analyst, an MSSP, or a CISO.
For SOC Analysts
Streamline Alert Handling: Studies have shown that most SOC teams feel overwhelmed by the volume of alerts they deal with. Security automation helps you work smarter, not harder by automating tedious and rote tasks so that analysts can focus on real threats instead.
Automate Triage: Unify all your alert sources into a single manageable queue, enriching IOCs with threat intelligence sources, past incident data, and malware detonation sandboxes. By auto-closing false positives and assigning a risk score to genuine threats, analysts can tackle high-priority alerts first.
A Better Digital Workspace: Consolidate important data from across the environment to get the information you need and do complex investigations faster without alt-tabbing and swivel chairing.
Improve accuracy: Security automation enables security teams to automate repeatable processes and combine the rigor of checklists and the precision of computing. Reduce the risk of human error, and improve the speed and consistency of your incident response.
For Security Leaders
Improve SOC Metrics: Cyber security automation drastically reduces the time it takes to detect and respond to incidents by eliminating tedious manual tasks in the triage stage. One of our enterprise customers was able to improve MTTR by 10x by leveraging our Event Pipeline.
Enhance Investigative Capabilities: SOC resources can contribute well beyond their experience level and do threat hunts by leveraging SOAR playbooks. Built-in case management, dashboards, and reporting capabilities enable analysts to collaborate and share information securely with resources both within and outside the SOC.
Reduce Employee Turnover: Monotonous and repetitive tasks are the ultimate joy thief and they ultimately lead to burnout and turnover. By eliminating tasks that nobody wants to do, it gives your team room to focus on more fulfilling work.
Eliminate Data Silos: A cybersecurity automation platform like Smart SOAR can be the connective layer that brings your entire stack together, regardless of the vendor or product type.
What Are The Types of Security Automation?
Security automation can be broadly classified into three main categories. Each type of security automation has its own strengths and weaknesses, and the right type of security automation will depend on the needs and resources of the security team. However, regardless of the type of security automation used, the goal is always the same: to improve the efficiency, accuracy, and scalability of security processes, and to better protect systems and data from threats.
Full-code security automation refers to tools that require users to write code in order to automate security tasks. It’s best suited for teams that have the time, resources, and expertise to build and maintain automation scripts.
No-code security automation requires little to no programming skills to implement. These tools typically have pre-built templates and drag-and-drop interfaces that allow users to automate security tasks without writing any code. No-code security automation is ideal for teams that are constrained by limited developer resources and expertise. While these may offer quick results, they are not as customizable or configurable and may not meet every edge case.
Low-code security automation provides a visual interface for automating security tasks and gives users the flexibility to write code if needed. It’s ideal for teams that don’t have the time to build and maintain complex automation scripts from scratch and want the best of both worlds. (In case you’re wondering, Smart SOAR belongs in this category)
What Are Some Examples of Security Automation Use Cases?
Security automation use cases range from threat detection and response, compliance and auditing, and infrastructure management. Implementable use cases depend on the other security technologies and systems in use, such as SIEM, EDR, XDR, firewall, NDR, threat intelligence tools, etc. Here’s a non-exhaustive list of security automation use cases:
- SIEM Alert Enrichment: Enhancing SIEM alerts with additional context and information.
- Phishing: Identifying and stopping malicious emails that mimic trustworthy sources.
- Ransomware: Detecting and mitigating ransomware attacks that encrypt sensitive information.
- Cryptojacking: Preventing unauthorized mining of cryptocurrency on endpoints and cloud infrastructure.
- Endpoint Incident Response: Automated response to security incidents on endpoints.
- Breach and Attack Simulation: Test and evaluate the readiness of your security tools against cyber threats.
- Malicious Insider Threats: Detecting and mitigating threats from malicious insiders.
- Malware Analysis: Automated sandboxing and analysis of malware samples.
- Suspicious Login Alerts: Detecting and alerting on suspicious logins.
- IOC Lookups: Automatically search for Indicators of Compromise (IOCs) in security alerts.
- Vulnerability Management: Automating the management and mitigation of vulnerabilities in the network.
- Domain Squatting: Detecting registration of domain names that mimic your organization’s brand names.
- Brand Protection: Automated protection of brand and intellectual property from digital threats.
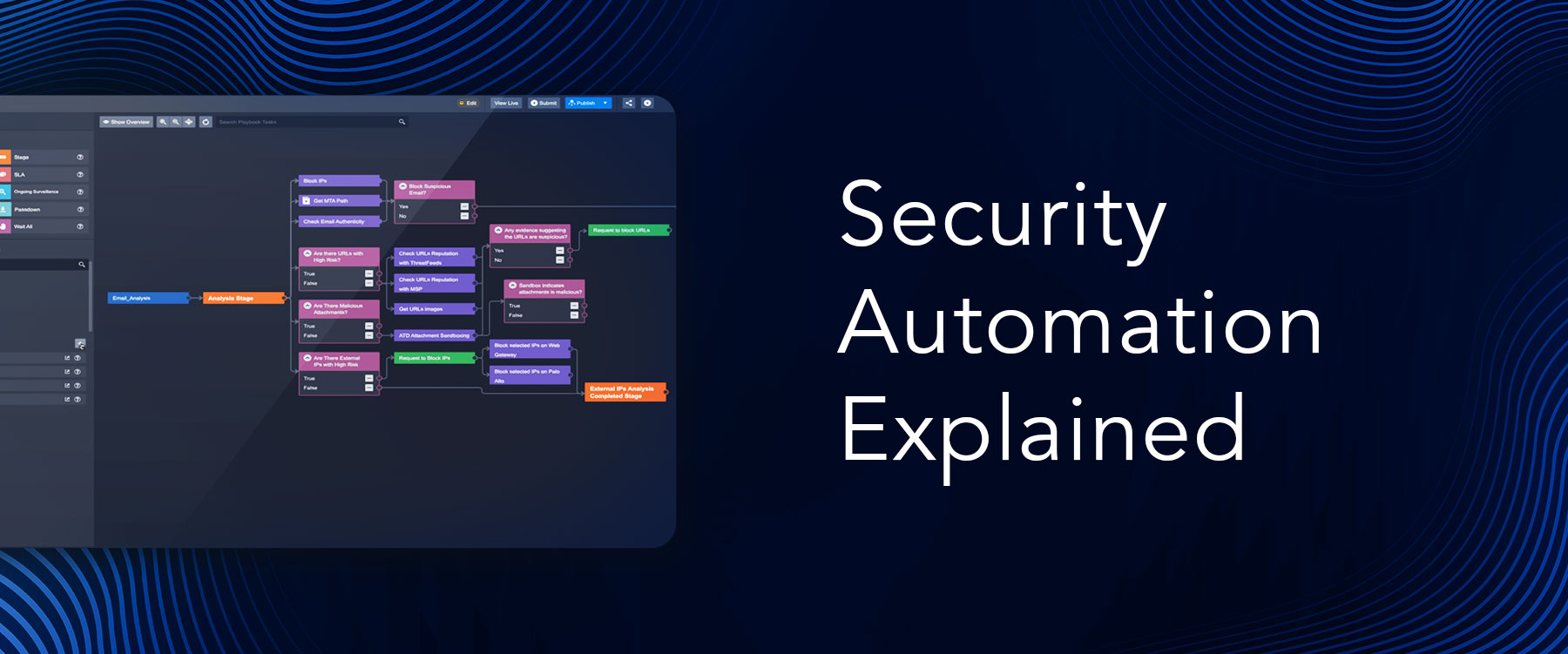
Watch this video to learn how to prevent breaches and downtime with Smart SOAR’s automated phishing incident response and threat detection playbooks. For more examples of SOC automation, check out this curation of SOAR playbooks.
Go Beyond Security Automation With Smart SOAR
Sure we can help you with your security automation needs. You’ll love our drag-and-drop playbook editor, which comes with a library of playbooks and hundreds of utility commands. But we can do more than that. As an end-to-end incident response solution, Smart SOAR can detect MITRE ATT&CK events across various systems, and correlate and mitigate events across multiple platforms. Event Pipeline, unique to Smart SOAR can automate nearly all the responsibilities of a tier-one or tier-two analyst. Sign up for a demo to learn why leading enterprises and MSSPs choose our Smart SOAR solution.