Many SOAR users find themselves frustrated with inflexible playbook builders that often require extensive manual intervention to accommodate unique or complex workflows. Such rigidity in automation tools can lead to inefficient incident responses, as security teams are forced to spend precious time filling in the gaps that their automated workflows cannot complete. This not only slows down their operational pace but also introduces a greater margin for error, as continuous manual adjustments can compromise the integrity and effectiveness of security protocols.
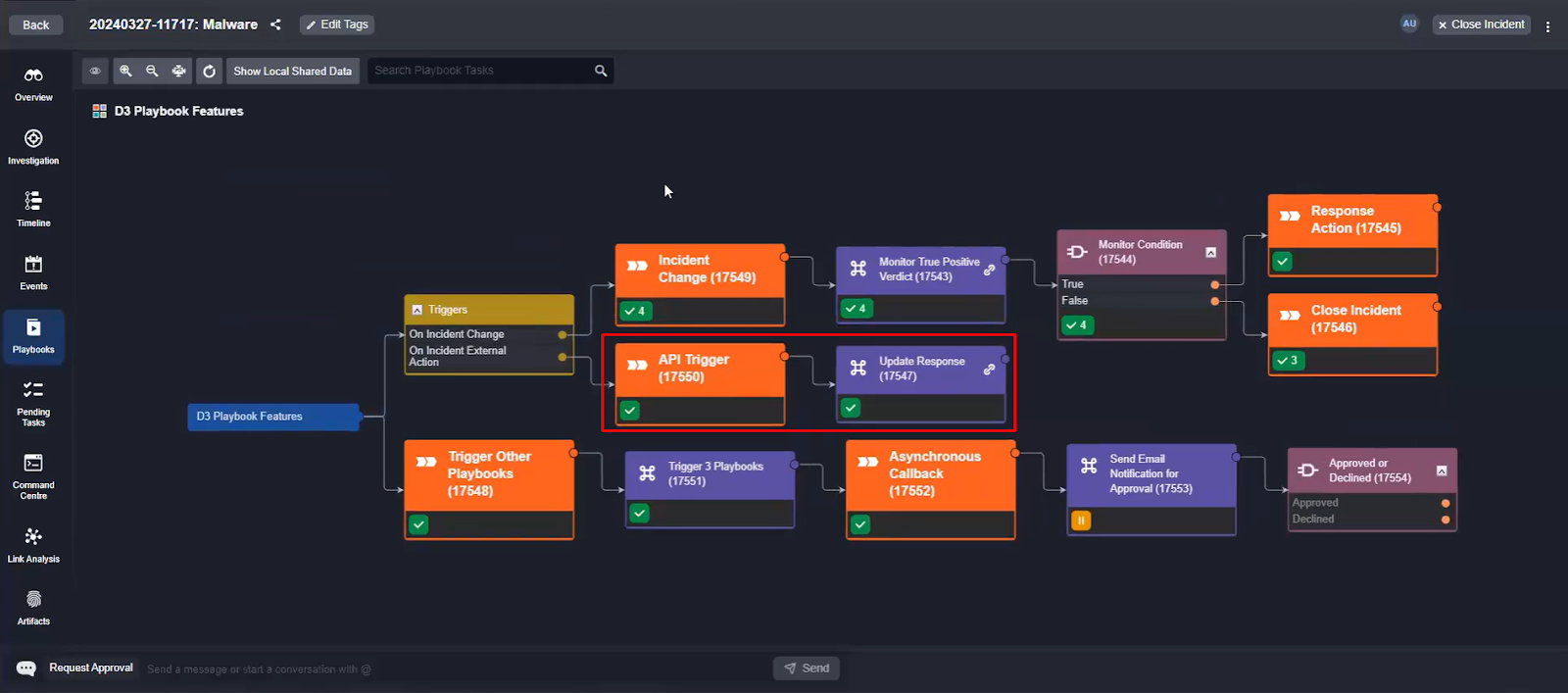
Playbook triggers, which activate automated response workflows in Smart SOAR, are built in order to increase the number of use-cases that the system can accommodate. As shown in the dark blue task below, there are six incident triggers that can be used to run unique workflows. In this article we will go over a few of them.
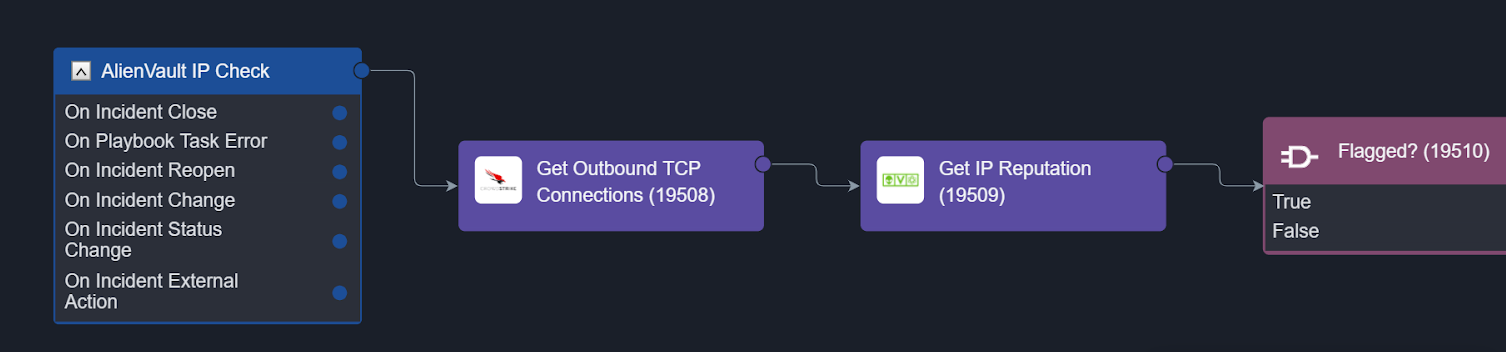
On Incident Change
When an important change is made to an incident, the On Incident Change trigger activates and runs a specific workflow. In this example, an analyst classifies an incident as a true positive, which activates a workflow with unique response actions for this type of incident. If the analyst had selected ‘false positive’ in this scenario, a different workflow would have been activated. The On Incident Change trigger is used to complement human actions on an incident with automated workflows that can assist with enrichment, correlation, response, recovery, or reporting. This is another example of how automation-assisted incident response is enabled in Smart SOAR.
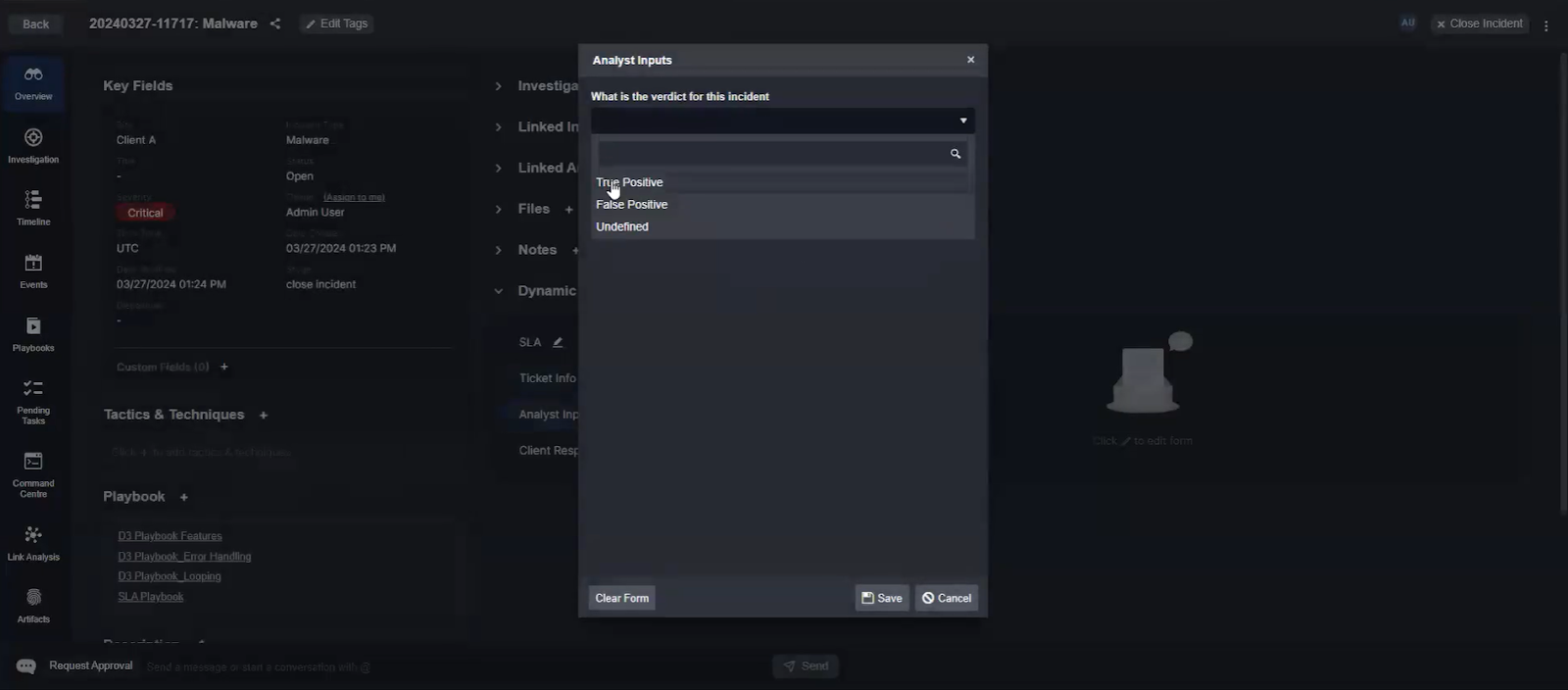
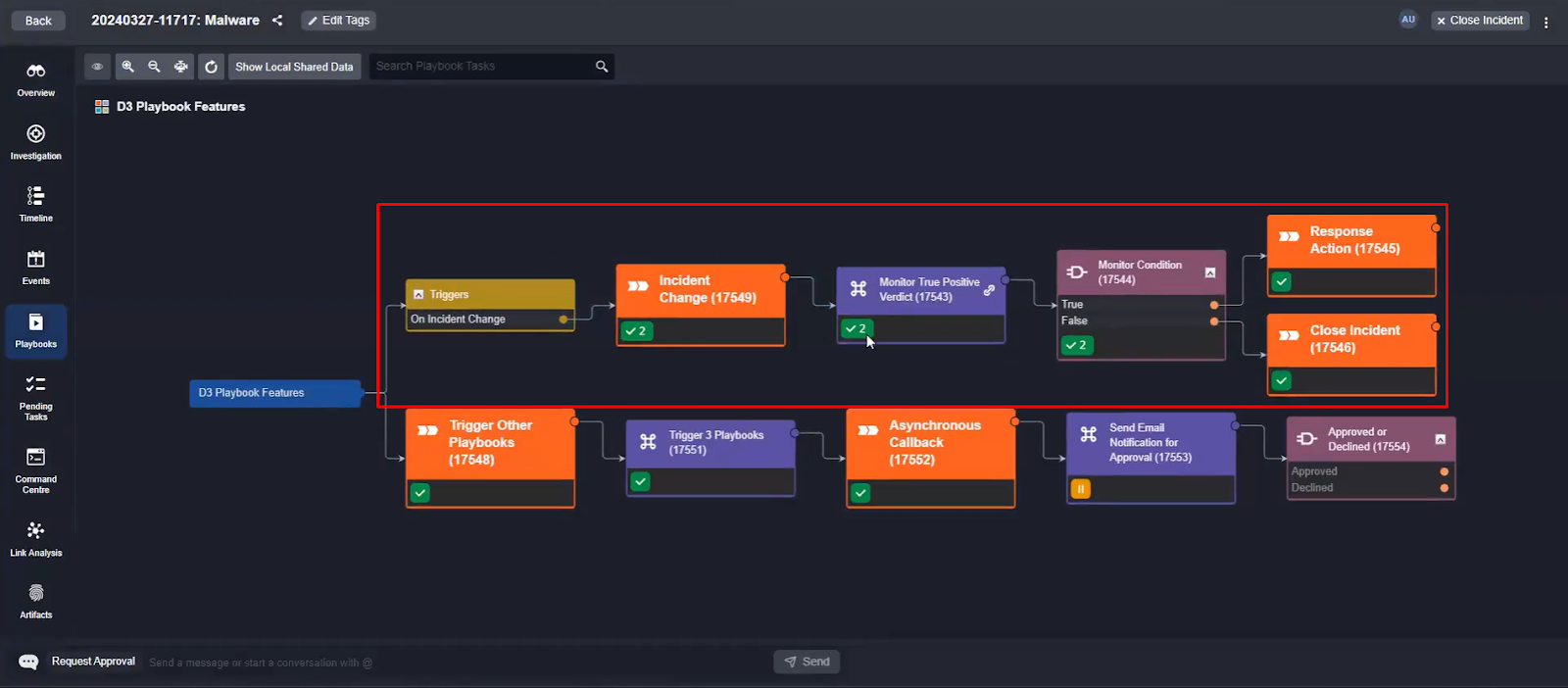
The On Incident Change trigger can activate multiple times. If, for example, the incident is classified as a false positive, but then later reopened and tagged as a true positive, the workflow will trigger both times. This ensures the correct workflow activates regardless of how an incident is processed.
On External Action
In cases where input from external parties is necessary, the On External Action trigger proves useful. For instance, when a client or external team needs to approve an action, they can submit their decision via a Google form. This form pushes data directly to the incident via an API, initiating the corresponding workflow.
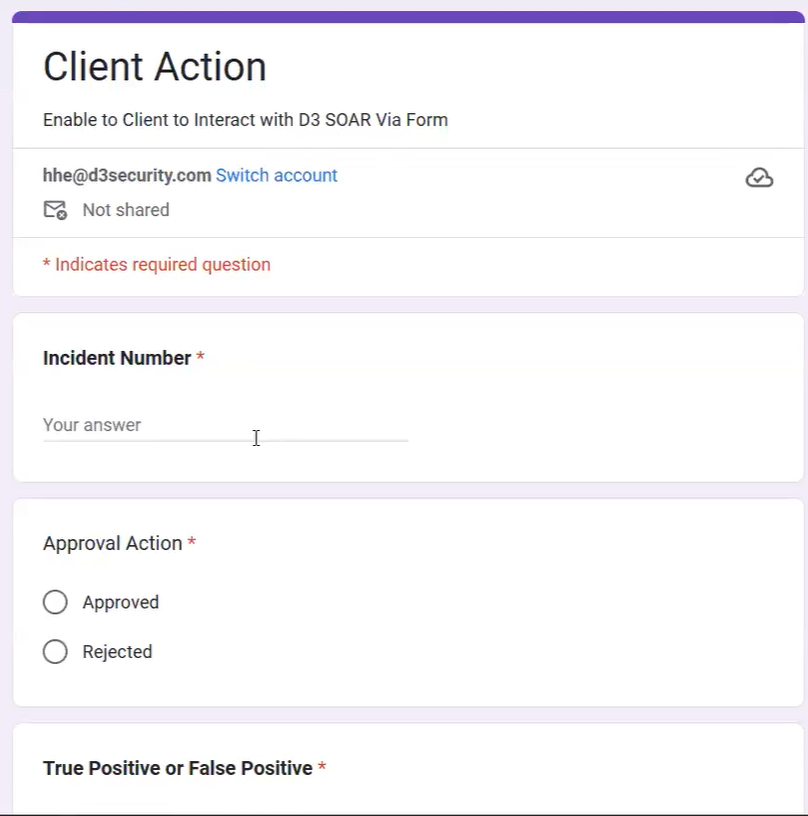
The feedback from the client can be easily formatted and displayed to the incident.
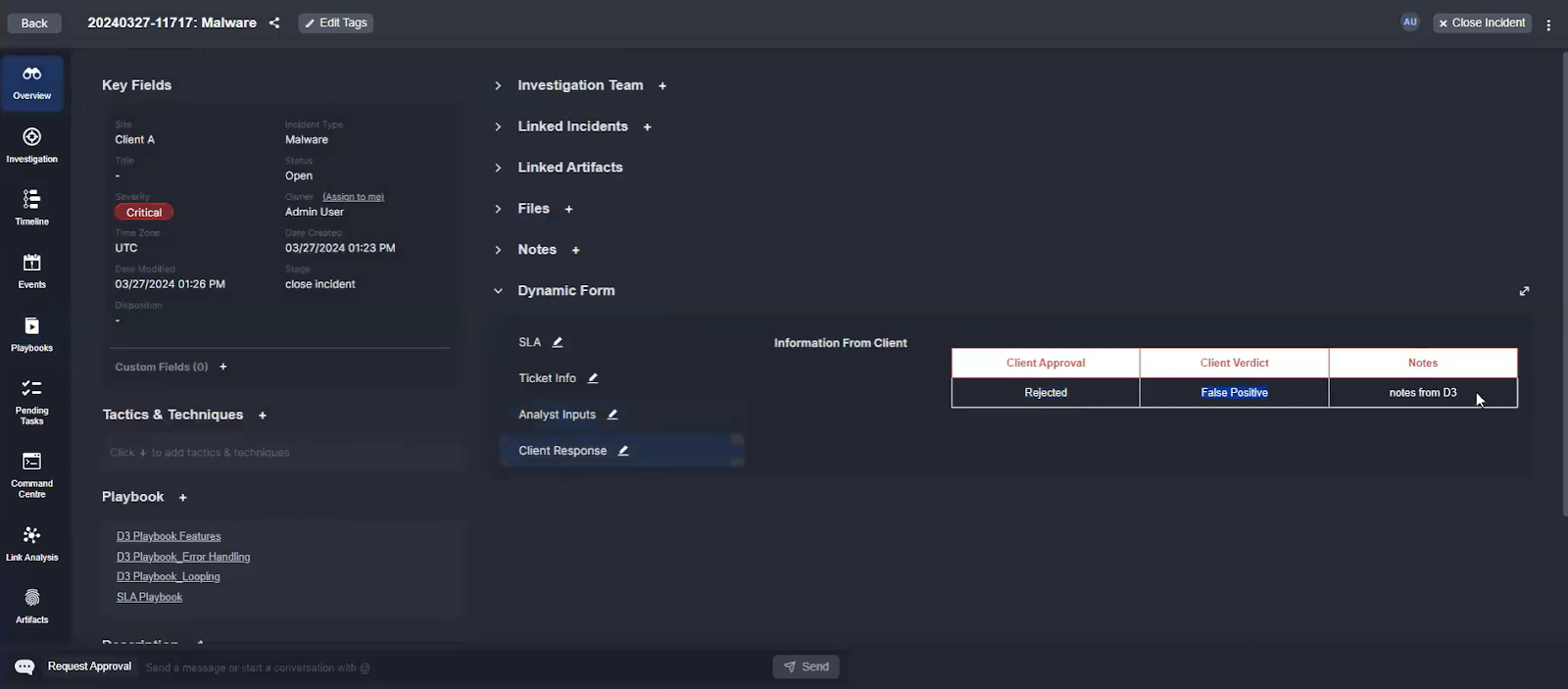
This process ensures that external feedback is integrated swiftly and efficiently, enabling a seamless flow of information and facilitating a collaborative response effort. Like the On Incident Change trigger, this can be triggered multiple times for the same incident, ensuring continuous integration of external inputs throughout the incident lifecycle.
On Playbook Error
Encountering errors within playbooks can potentially disrupt security operations. The On Playbook Error trigger is specifically designed to promptly address such issues.
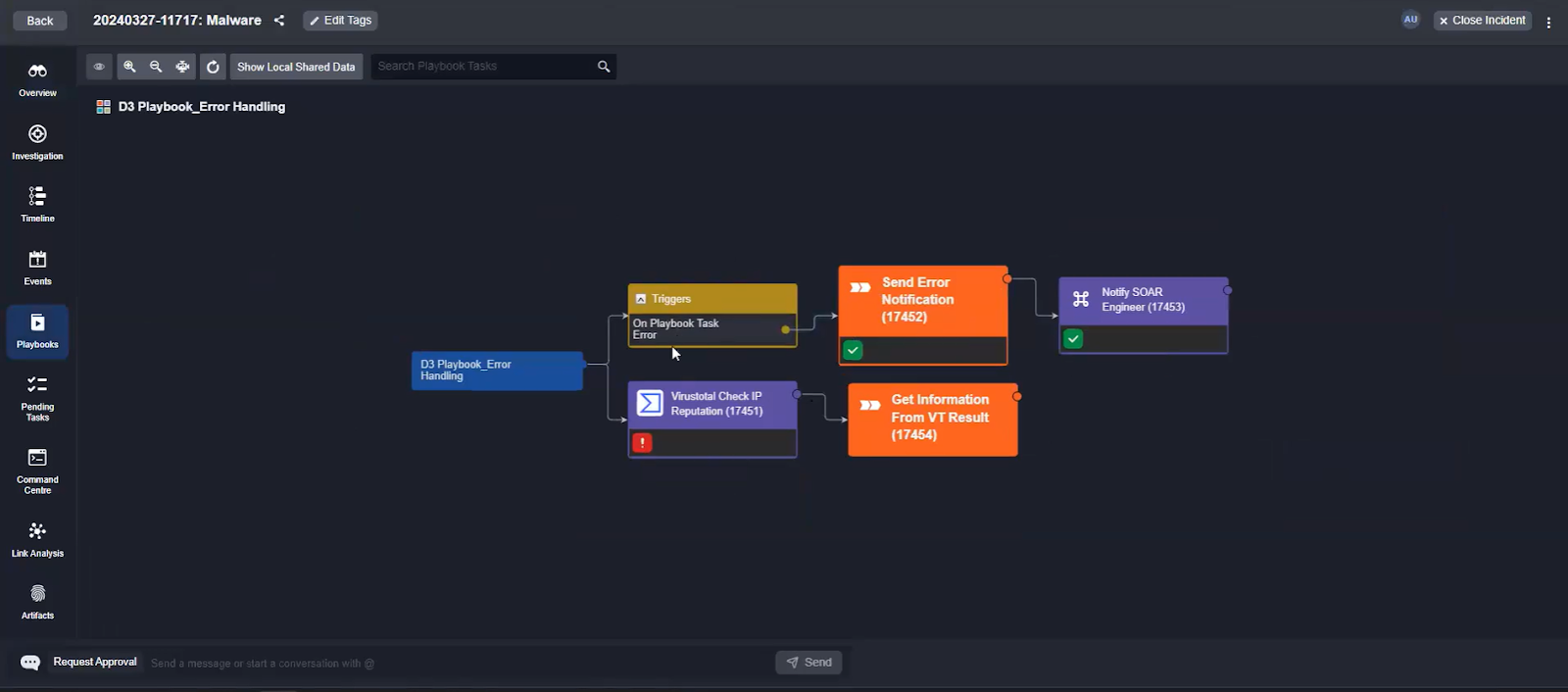
Upon encountering an error, this trigger initiates a workflow that can involve modifying the task, re-testing the playbook, or notifying a SOAR engineer. This rapid response capability minimizes downtime and ensures that operational continuity is maintained, safeguarding against potential security lapses.
Takeaways
The diverse triggers within Smart SOAR’s playbook engine offer users flexibility and control over their security operations. By accommodating an extensive range of use cases—from error handling to external collaboration—these triggers ensure that security teams can adapt quickly to changing needs.




